-
Phone
-
E-mail
-
Whatsapp
The machinery steel industry is undergoing remarkable transformations. Innovations are reshaping production processes and enhancing material properties. According to a recent report by MarketsandMarkets, the global machinery steel market is projected to reach $150 billion by 2025, driven by advancements in technology and increasing demand across various sectors.
Current innovations in machinery steel focus on high-strength and lightweight materials. These developments aim to improve efficiency and reduce overall costs in manufacturing. For example, specialty steels are now exhibiting exceptional fatigue resistance. Companies are investing heavily in research to push the boundaries of what machinery steel can achieve. However, the industry faces challenges. While technology is evolving, it may not be keeping pace with rising sustainability expectations.
The emergence of heat-resistant alloys has opened new avenues for machinery applications. Reports show that such materials can withstand high temperatures and enhance performance. Adapting to these innovations requires careful consideration of production methods and costs. As the industry embraces change, it must also reflect on environmental impacts and strive for better practices. Balancing progress with responsibility will be key to the future of machinery steel.

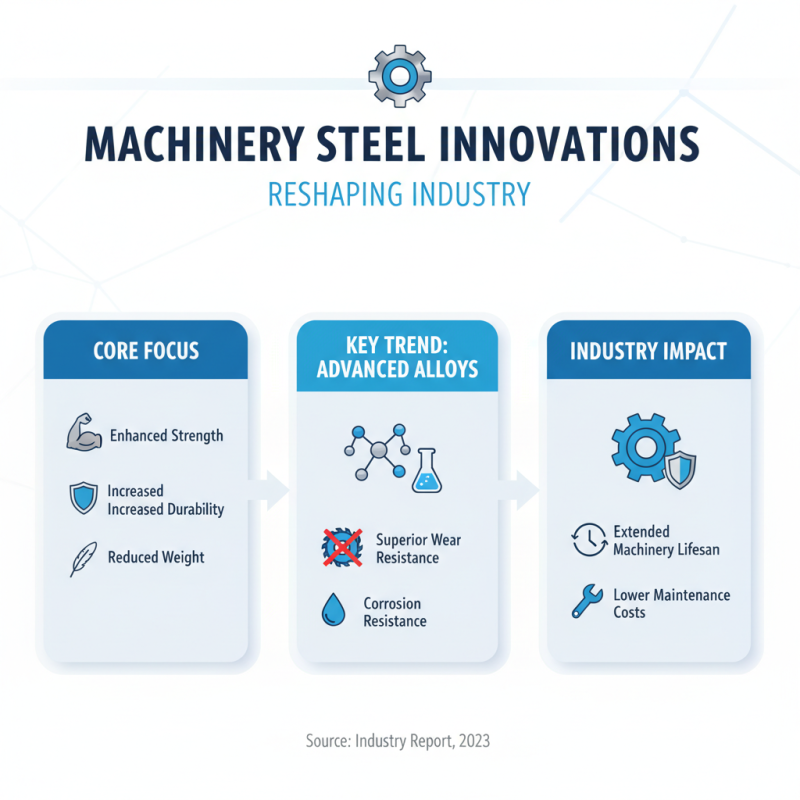
Emerging trends in machinery steel innovations are reshaping the industry landscape. The focus lies in improving strength and durability while minimizing weight. One notable trend is the development of advanced alloys. These materials exhibit superior resistance to wear and corrosion. Thus, they extend the lifespan of machinery, reducing maintenance costs.
Another key aspect involves smart steel technologies. Sensors embedded within steel structures monitor performance in real-time. This allows for immediate responses to stress and environmental changes. Efficiency can be significantly improved through these smart solutions. However, the integration of technology raises concerns about complexities in operations. The dependency on digital systems needs careful consideration.
Sustainability is another driving force behind these innovations. Many companies are exploring eco-friendly production methods. This includes recycling scrap steel and utilizing renewable energy sources during manufacturing. The path to greener practices is still challenging, but progress is being made. Balancing performance with environmental responsibility is crucial, but not always straightforward. The industry must address these contradictions to fully embrace innovation.
The use of advanced alloys has significantly shaped the machinery industry. These innovative materials enhance strength and durability. Many engineers are now exploring high-performance steel formulations to meet demanding applications. The right combination can improve fatigue resistance and reduce weight. This leads to more efficient machinery.
However, the process of integrating these alloys is not without challenges. There can be issues with manufacturing and machining due to their unique properties. Some companies struggle to adapt their production lines to new materials. Misaligned expectations often lead to wasted resources and time.
The ongoing research into advanced alloys promises exciting possibilities. Engineers are focusing on how to optimize these materials further. They aim to ensure compatibility with existing technologies. Addressing these challenges will be essential for maximizing the benefits. As the machinery landscape evolves, innovation must be coupled with practical solutions.
The steel production industry faces significant challenges. Increasing pressure to adopt sustainable practices is one of them. Machinery manufacturers are rethinking their supply chains. They focus on reducing carbon footprints and increasing energy efficiency.
Using recycled steel is one way to make a difference. It helps lower greenhouse gas emissions. However, many manufacturers still rely heavily on virgin materials. This inconsistency in practices raises questions. Are we doing enough to promote sustainability in steel?
Tips: Consider evaluating your supply chain. Seek suppliers who prioritize sustainability. Engage in open discussions about carbon reduction goals.
Another critical area is waste management. Effectively recycling waste steel can save resources. However, companies often overlook this aspect. Improving waste management could reduce overall production costs. It also enhances environmental impact.
Tips: Regularly audit your waste management processes. Identify opportunities to recycle and repurpose materials. Set measurable goals to track improvements.
The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) in steel production is reshaping the landscape of the industry. AI technologies are streamlining operations and enhancing productivity. For instance, a report by the World Economic Forum states that manufacturers leveraging AI can expect up to a 20% increase in productivity. This is significant, especially as the steel industry faces higher demand and rising costs.
Real-time data analytics plays a vital role in this transformation. AI systems analyze complex datasets from production processes, leading to better decision-making. These systems can predict equipment failures, reducing downtime by as much as 15%. However, this reliance on technology raises concerns about cybersecurity risks. Steel producers must address potential vulnerabilities to protect their operations.
Moreover, while AI can optimize the supply chain, it requires significant upfront investment. Many smaller manufacturers struggle with funding. They often lack the resources to implement advanced technologies successfully. This gap could widen the divide between large firms and their smaller counterparts, leading to greater challenges in the sector. Embracing innovation is crucial, but it demands careful consideration regarding sustainability and inclusivity.
| Innovation | Description | Impact on Production | Adoption Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| AI-driven Process Optimization | Utilizing AI algorithms to enhance production efficiency and reduce waste. | Increased efficiency by 15% and reduced operational costs. | 60% |
| Predictive Maintenance | Data analytics to foresee equipment failures before they occur, preventing downtime. | Reduced machine downtime by 30%. | 45% |
| Advanced Robotics | Use of robotic technology for precision tasks in steel manufacturing. | Enhanced production speed and accuracy, leading to a 25% output increase. | 70% |
| Blockchain for Supply Chain Transparency | Implementation of blockchain to ensure traceability and authentication in the supply chain. | Improved supply chain efficiency and reduced fraud costs. | 30% |
| Digital Twin Technology | Creating digital replicas of physical assets to analyze performance and optimize process. | Enhanced simulation capability leading to better design and operation decisions. | 50% |
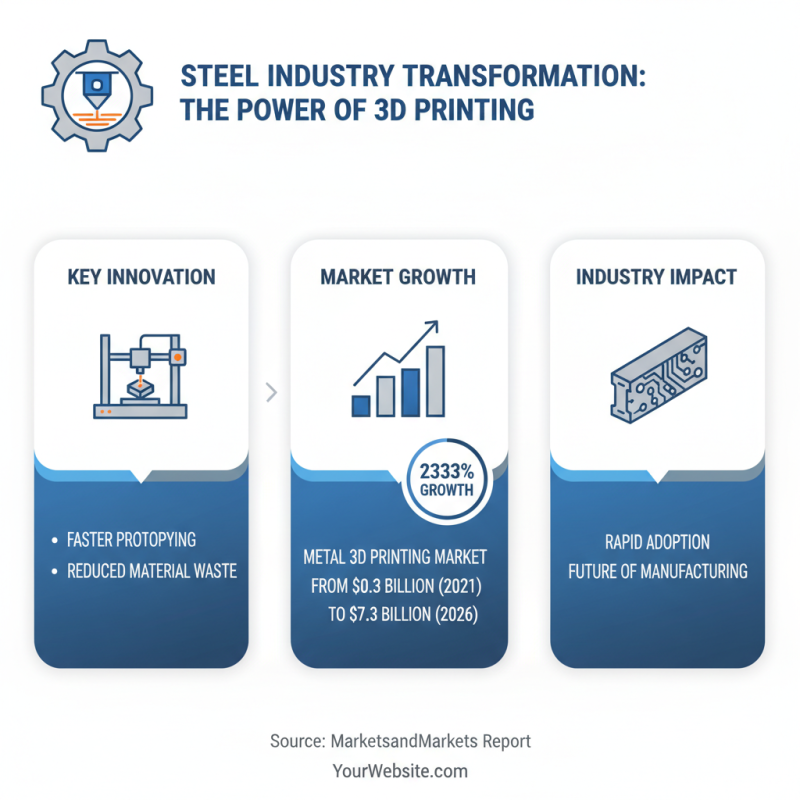
The steel industry is undergoing significant changes. One of the main drivers is 3D printing technology. This innovation allows faster prototyping and reduced material waste. According to a report by MarketsandMarkets, the metal 3D printing market is expected to grow from $0.3 billion in 2021 to $7.3 billion by 2026. Clearly, this technology is gaining traction.
3D printing offers incredible design flexibility. Complex geometries are achievable, which traditional methods often cannot produce. Manufacturers can create lightweight parts that do not compromise strength. However, challenges remain. The cost of equipment is high, and material options are limited. Not all steel grades are suitable for 3D printing. This can slow down wider adoption in the industry.
Looking ahead, 3D printing could transform supply chains. Companies may need fewer parts in stock, leading to lower inventory costs. Still, companies must invest in R&D to address issues like quality control. Maintaining consistent standards is crucial as the field evolves. The potential is enormous, but reflection on these hurdles is necessary for success.